What is audio restoration?
This article introduces the field of audio restoration, with a focus on the techniques, tools, and software available. We will therefore look at the different types of sound defects as well as other problems such as background noise and distortion. Each defect will therefore be defined and followed by specific advice to resolve them.
Understanding Audio Restoration
• Definition of audio restoration and its main applications.
Restoring audio involves improving the sound quality of altered or damaged recordings. It finds its main applications in the music industry, cinema or sound archives. Audio restoration aims to eliminate unwanted noise, such as hiss, clicks, pops, and to correct sound defects such as frequency and phase issues. It can also restore damaged recordings by removing clicks, pops and other imperfections.


By using specialized techniques and tools, this recovers quality recordings and preserves their authenticity. This helps improve the listening experience for listeners by eliminating unwanted sound distractions. Audio restoration is therefore a meticulous process that requires technical expertise and an attentive ear. Audio professionals therefore use advanced audio restoration software and specialized equipment.
In short, audio restoration is therefore essential to preserve and restore all types of audio files and therefore improve the sound quality of productions and offer an immersive and enjoyable listening experience.
• Explanation of the different types of audio problems encountered.
Audio restoration faces different types of audio issues that can have a significant impact on sound quality. Unwanted noises, such as hiss, clicks, pops, and pops, can creep into recordings, disrupting listening. Phase problems also lead to inconsistent sound reproduction.


Damaged or degraded recordings may therefore exhibit defects such as crackles, clicks, playback skipping or signal dropouts. These audio problems can affect the perception and appreciation of music or sound in general. Thanks to advanced techniques and specialized tools, it is possible to restore damaged recordings and make them more pleasant to listen to.
Audio restoration techniques
• Elimination of unwanted noise (background noise, hiss, etc.)
Several techniques are used to eliminate unwanted noise during audio restoration. The first method is filtering. Specific filters, such as high pass and low pass filters, are applied to attenuate unwanted frequencies. This reduces background noise and improves sound clarity.


Another common technique is the use of equalization. By adjusting the levels of specific frequencies, it is possible to reduce extraneous noise such as sibilance and improve tonal balance. Noise suppression is also an effective approach. It involves analyzing unwanted noise and removing it using advanced noise reduction tools.
Finally, restoration techniques can be combined to achieve optimal results. For example, a combination of filtering, equalization and noise suppression can therefore be used to eliminate various unwanted noises simultaneously.
• Lists of sound faults
- Clicks: Sudden short volume spikes in the recording, usually caused by imperfections in the media or transfer errors. They can be eliminated by using click removal tools or by manually editing the affected areas.
2. Pops: These are audible impulse noises, often caused by dirt or imperfections in the recording medium. They can be reduced or removed by using pop reduction tools or editing the affected parts.
There are different variations of pops, including explosive or plosive pops, which occur when words containing hard consonants in front, such as the consonant “p”, are spoken.
If you’re using a sensitive microphone, like a ribbon microphone, those harsh consonants can cause damage. A pop filter will therefore be required.
3. Crackles: These are “creaking” or “sizzling” type noises, usually caused by surface problems or deterioration of the substrate. They can be repaired by using noise reduction tools or by performing a manual restore.
They can also be related to misconfiguration of the buffer (buffer) and sample rates. I plan to write a full article on this topic soon.
• Other sound defects
4. Clipping: This is distortion that occurs when the audio signal exceeds the limits of the recording system. First, to resolve clipping, it is therefore important to set the recording levels correctly. Second you can use limiting or compression tools to smooth out excessive peaks.


5. Digital artifacts: These are sound anomalies caused by compression or digital-to-analog conversion. To mitigate them, one can use artefact reduction algorithms or adjust the conversion parameters.
6. Sibilance: These are unwanted frequencies from the pronunciation of “s” and “t” that can appear in the voice recording. They can be reduced by using high-cut filters, dynamic eq or specific noise removal tools like a De-Esser.
Free song analysis
FreeMastering Sample
Audio restoration tools
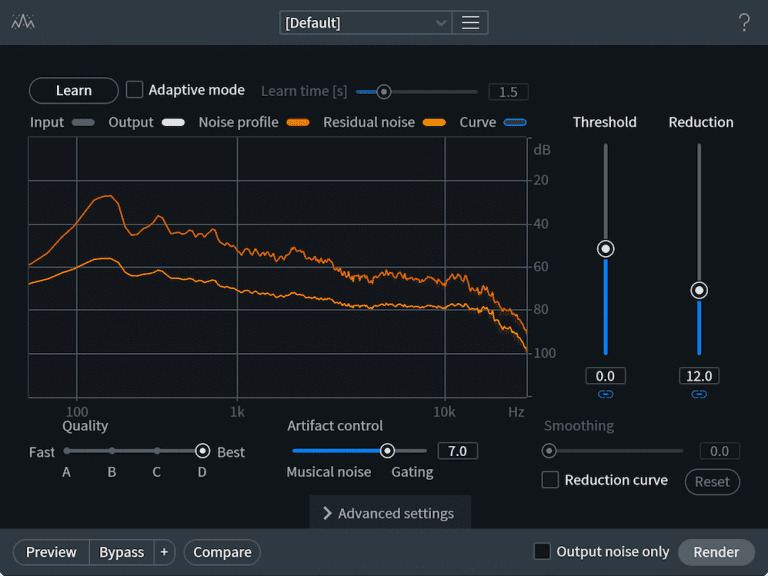
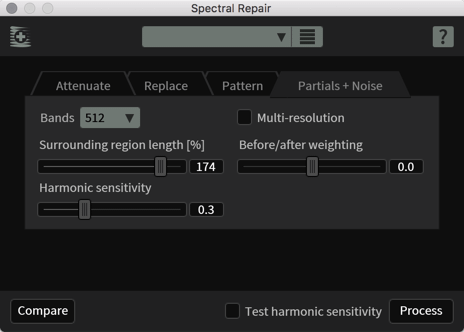
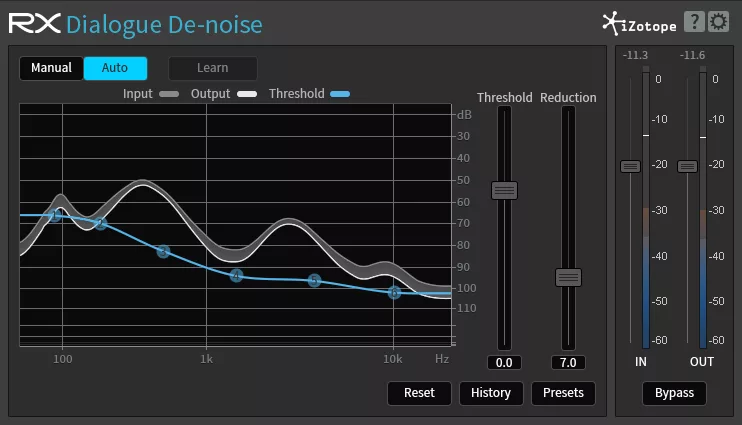
• iZotope RX
- Denoise (Noise Reduction): Eliminates unwanted noise such as hiss, background noise, crackling, etc. It uses advanced algorithms to attenuate noise without compromising the quality of the audio signal.
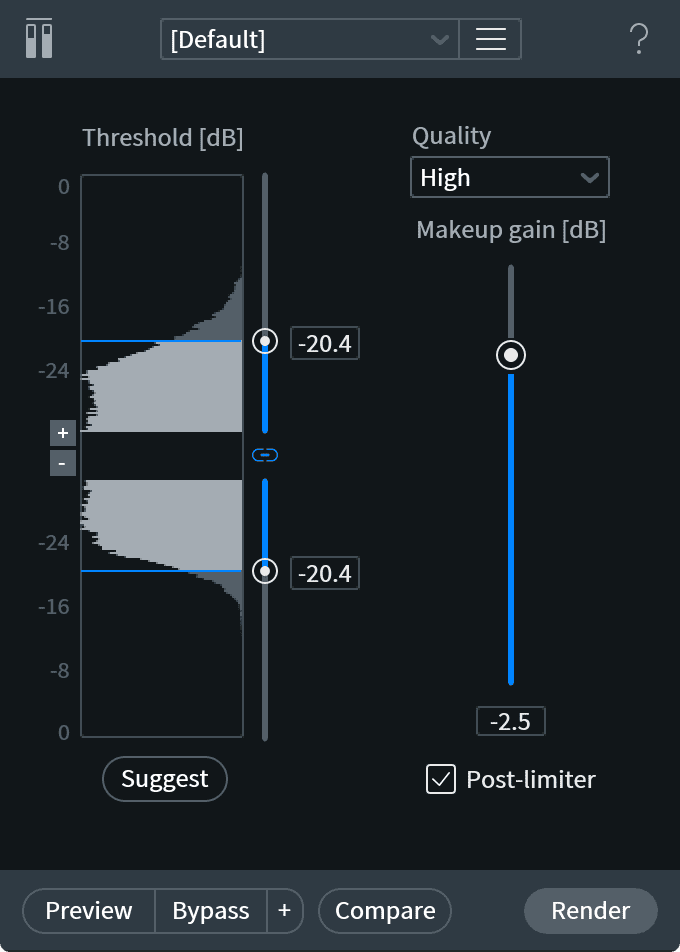
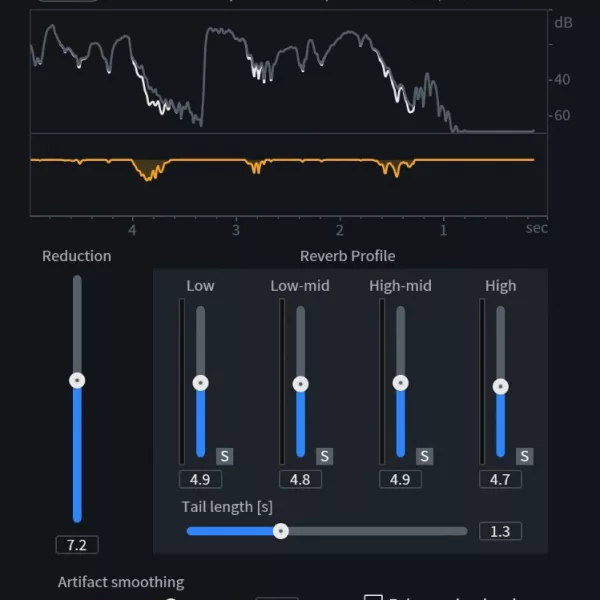
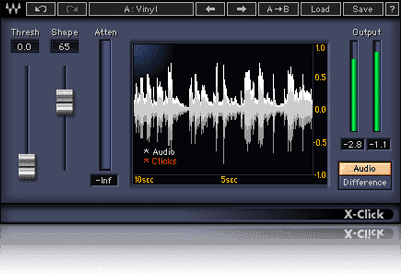
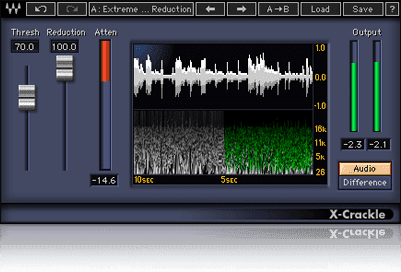
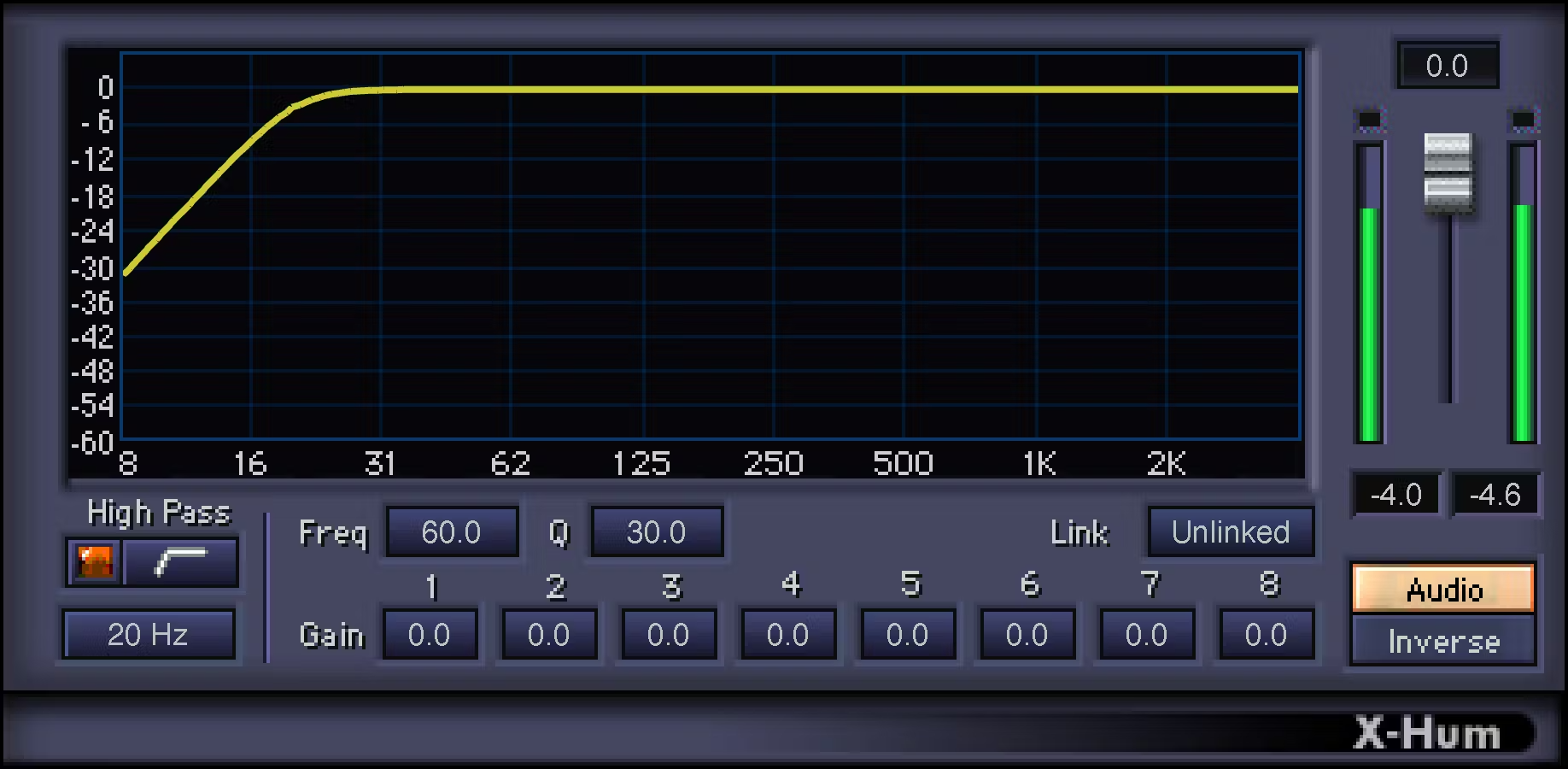
• Waves Restoration
- X-Click : Helps remove unwanted clicks that may appear in audio recordings, such as those caused by equipment faults or digital synchronization issues.
- Le X-Crackle : This feature is designed to eliminate crackling and crackling present in audio recordings, usually caused by defects in the source or recording medium.
- X-Hum : Helps reduce unwanted hum and hum, such as those caused by electrical interference or grounding issues.
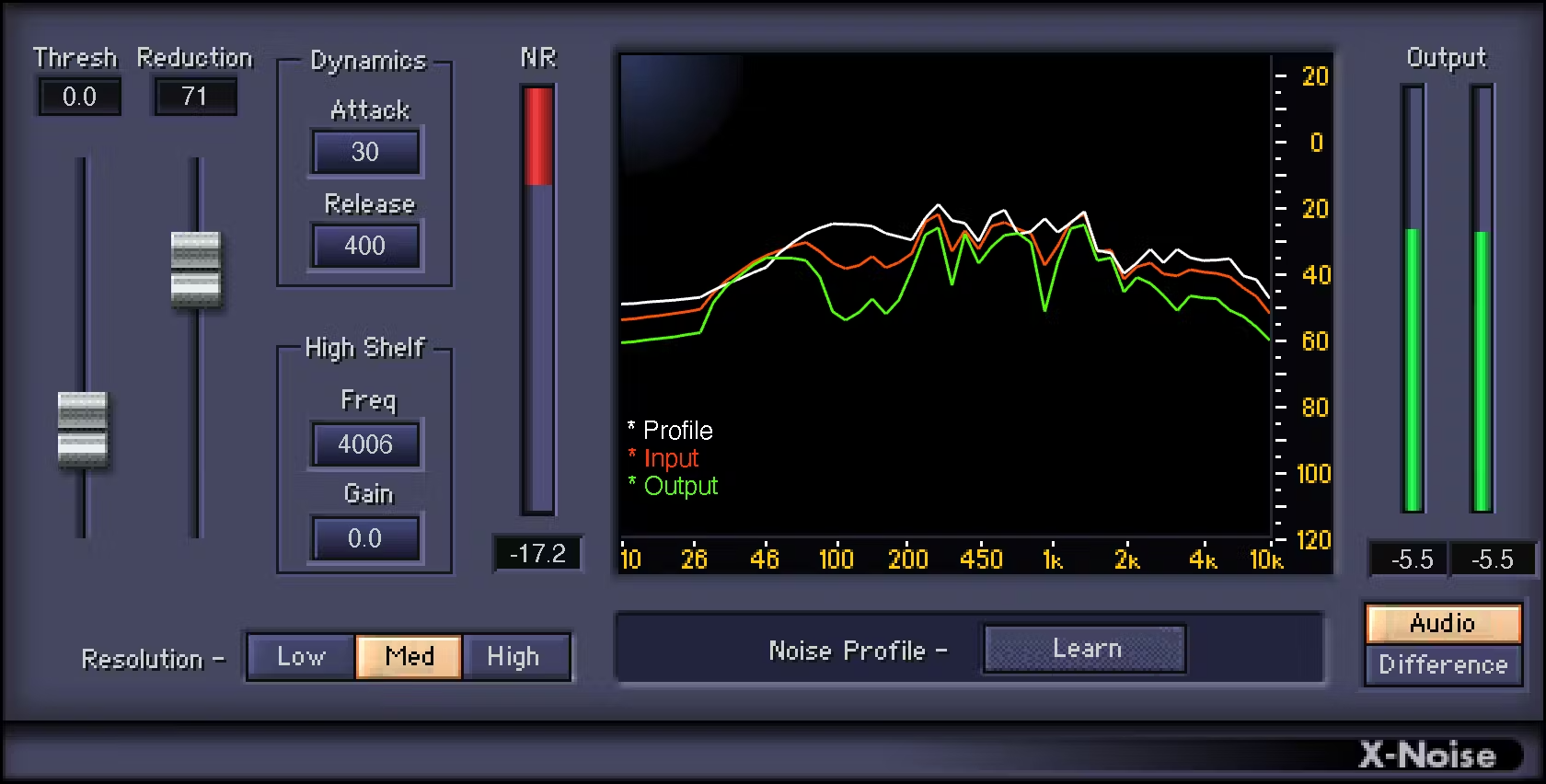
- X-Noise : This feature is designed to reduce constant and unwanted background noise in audio recordings, such as hiss, ambient background noise, etc.
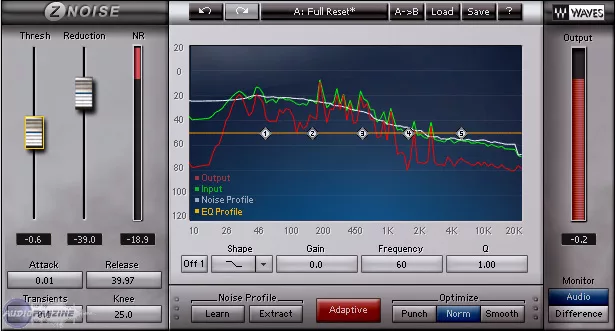
- Z-Noise : Offers more advanced noise reduction by using adaptive algorithms to eliminate background noise without altering the main audio signal.
Each function of Waves Restoration is therefore designed to target and solve specific audio restoration problems, providing users with a range of specialized tools to improve the sound quality of recordings.
In conclusion, audio restoration is an essential area of sound production, offering tools and techniques to improve the quality of recordings and therefore repair damaged recordings.