Analog vs digital: what are the differences?
The article introduces the differences between analog and digital technologies. In a field where the technical possibilities are vast, understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each approach is of great relevance. Decisions made about whether to use analog or digital equipment can have a significant impact on sound. By exploring the differences between these two distinct sonic worlds, we uncover the strengths and limitations of each method. This allows professionals to make informed choices.
The concepts that I bring in this article are summarized for the understanding of all. This subject being very vast I will make in the future more complex articles approaching each one of these subjects in depth.
What is analog and digital in the studio?
• Explanation of fundamental differences
Analog and digital equipment have fundamental differences in the studio. Analog gear provides a warm, organic sound through its physical components. Regarding digital equipment, they offer increased flexibility and precision thanks to their digital processing.
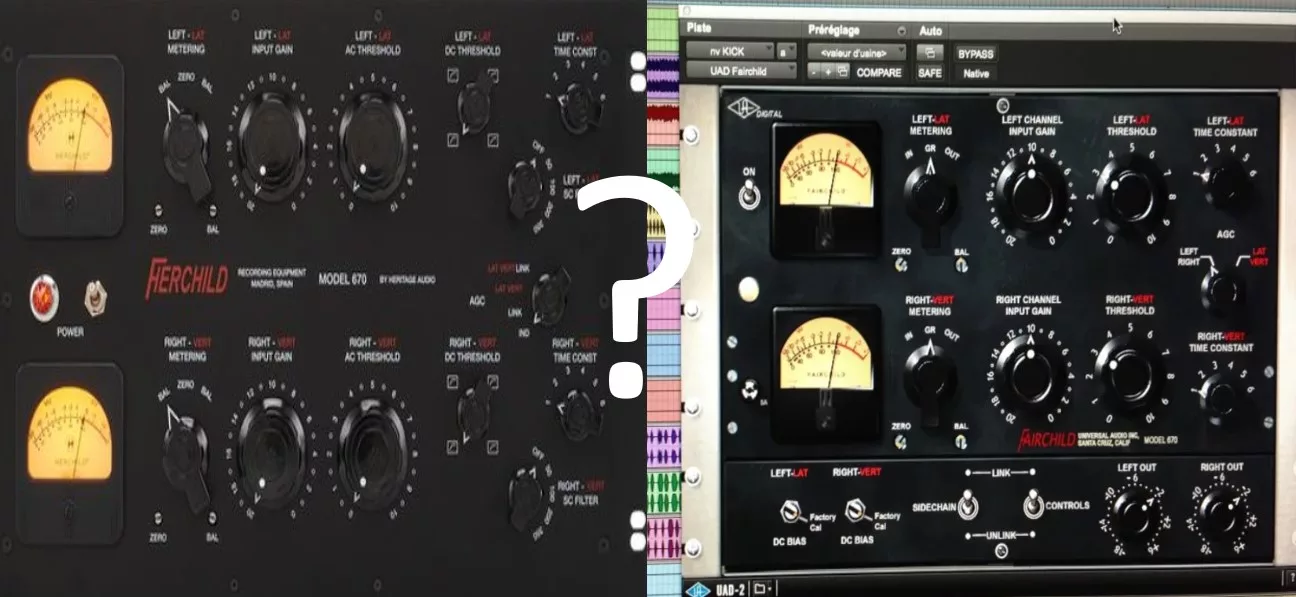

In terms of cost, analog equipment is generally more expensive, while digital equipment is more affordable. Choices between the two depend on sonic preferences, budget constraints, and specific project needs.
It is important to note that some sound engineers prefer to combine the two types of equipment to benefit from the advantages of both worlds.
• Presentation of the characteristics
Analog equipment is made up of different essential elements. First, it includes electronic circuits that process the audio signal analogically. These circuits are made up of components such as resistors, capacitors, amplifiers, tubes etc. They act together to shape and modify sound. Additionally, analog equipment can also feature transformers, which play a key role in changing signal levels and adding specific sonic characteristics.

Potentiometers and physical buttons allow you to adjust the various parameters of the equipment, such as volume, equalization, compression… These physical elements offer a tactile experience and great control precision. Finally, analog equipment has audio connections, such as physical inputs and outputs. All of these components form a coherent system that allows the processing and modification of the audio signal in an analog way.
The digital signal is processed by specific algorithms and software that perform various operations such as equalization, compression, reverberation, etc. These operations are carried out by digital signal processors (DSP) or by the CPU of your computer which performs the necessary calculations.
The results are then converted into an analog audio signal by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) to be heard. Graphical interfaces, available on computers or digital consoles, make it possible to control the parameters and effects applied to the digital signal. In sum, digital processing is based on the conversion, algorithmic processing and graphical control of the audio signal, offering greater flexibility and precision.
Advantages of analog in the studio
• Specific advantages offered by analogue equipment
Analog equipment can produce natural harmonic saturation (THD) through the various electronic components that add richness and complexity to the sound. This phenomenon contributes to create a pleasant harmonic sensation for the ear. When it comes to workflow, some sound engineers prefer the tactile and immediate nature of analog equipment.


Potentiometers and physical buttons adjust parameters in real time, providing an intuitive experience. In summary, analog equipment offers advantages such as natural harmonic saturation and a tactile, vintage workflow that appeal to many sound professionals.
• Situations where analog may be preferable to digital.
In some specific situations, the use of analog equipment may be preferable to digital ones. For example, analog compressors or certain passive EQs offer a random and organic reaction in terms of THD which creates subtle and natural variations in the processed signals. This unique characteristic can be difficult to replicate accurately using digital plugins, which tend to be more predictable and linear.
For example, analog summers are renowned for their ability to blend multiple audio signals seamlessly. They bring a certain color and cohesiveness that can be perceived as more pleasing and natural than that of digital summing.
Thus, in contexts where random reaction, subtle variation, or specific color are desired elements, analog equipment retains an edge over its digital counterparts. However, it is important to note that technological advancements continue to improve digital emulations. This brings the two worlds closer together, thus offering more flexibility and possibilities of choice to sound professionals.
Freesong analysis
FreeMastering Sample
Benefits of digital in the studio
• Presentation of the key advantages of digital equipment
Digital equipment offers several key benefits. First, they provide increased precision in audio signal processing. This is due to the manipulation of digital data with precise algorithms. In addition, their flexibility allows a wide range of manipulations and adjustments to be performed with great precision. Ease of handling is also a notable advantage. Parameters can be adjusted using user-friendly graphical interfaces on computers or digital consoles.
In addition, digital equipment makes it easy to save and recall settings. It is therefore very practical during subsequent work sessions. Finally, time effects such as reverb or delay can be applied with great precision and controlled in greater detail. In sum, the advantages of digital equipment include precision, flexibility, ease of handling, saving of parameters and precise control of temporal effects.
• Examples of cases where digital is more suitable than analog
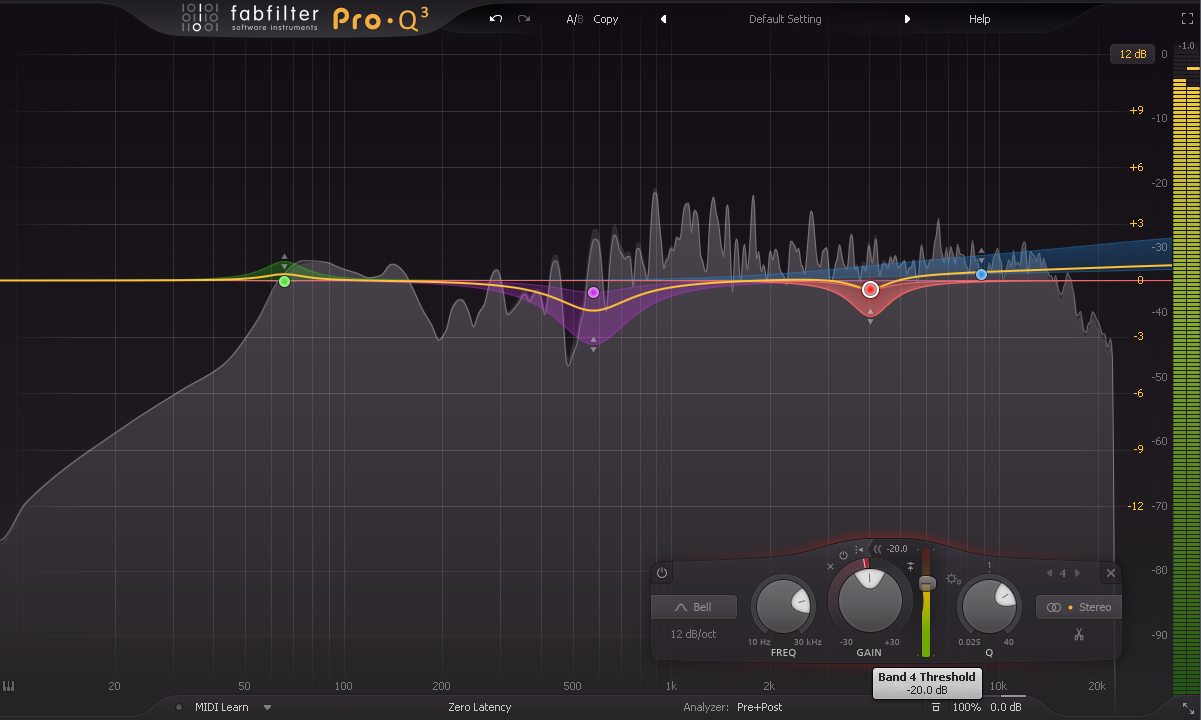
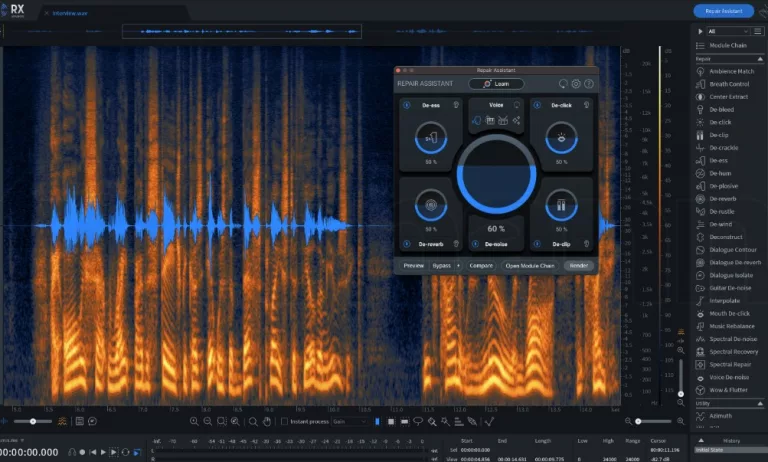
Digital equipment is often chosen because of its much more affordable cost. Advancements in technology have allowed the development of very powerful software plugins as we demonstrated in the previous Fabfilter Pro-Q 3 equalizer review. For example, audio restoration plugins like Izotope RX offer advanced features for reducing noise and the repair of damaged recordings.
Additionally, to give another example, convolution effects, available as plugins, allow you to recreate impulse responses from real environments, recording equipment, or world famous locations. This opens up endless creative possibilities. For example to add atmospheres, realistic reverbs and other immersive sound effects. Thus, digital equipment offers more economical and versatile solutions thanks to rapid technological progress.
Limitations of analog in the studio
There are some potential downsides to using analog to consider. First, analog equipment can lead to high costs. They often require high quality physical components and are more expensive to manufacture and maintain.
In addition, their maintenance can be complex, sometimes requiring specialized repairs. Another analog-related challenge is physical space management, as such equipment typically takes up a lot of room in a studio, requiring additional racks and cables.
Additionally, the physical limitations of analog equipment can make certain tasks more laborious, such as precise parameter recall or advanced automation.
Finally, mobility is an aspect to consider, since analog equipment is less easy to transport and configure in production environments outside the studio. Despite their distinct sonic qualities, there are therefore potential drawbacks to using analogue in terms of cost, maintenance, space management and mobility.
Limitations of digital in the studio
The use of digital equipment also has some specific disadvantages to consider. Latency, that is, the delay between signal input and output, can be a problem in some situations.


Digital artifacts, such as jitter or digital distortions, can also affect sound quality. Advances in technology have reduced these problems over time.
Additionally, digital controls can be perceived as less intuitive than the physical potentiometers of analog equipment. In summary, the disadvantages of digital equipment include possible artificial sound coloration, latency, digital artifacts, and loss of tactile feel to physical controls.
The choice between analog and digital in the studio
When deciding between using analog, digital, or a combination of the two in the studio, several factors must be considered. First, it’s important to consider personal preferences and artistic goals. Some sound engineers prefer the organic, vintage sound of analog, while others are drawn to the flexibility and precision of digital. Next, budget is crucial, as analog equipment can be more expensive to acquire and maintain.
In addition, the nature of the project can also influence the decision. For example, if a production requires quick and precise edits, digital may be more appropriate. On the other hand, if specific coloration is desired, analog may be preferable.


Finally, the combination of the two approaches can offer the best of both worlds, making it possible to take advantage of the specific advantages of each method.
Ultimately, there is no one-size-fits-all answer, and each studio should assess their needs and resources to make the best decision. Whether opting for analog, digital or a combination of the two, the ultimate goal is to achieve high quality sound and meet the demands of every musical project.